3 Essential Exercises For Runners to Prevent & Help With Shin Splints
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, is a common condition that affects runners and other athletes who engage in high-impact activities. It's characterised by pain along the inside of the shin bone, and can be caused by a number of factors, including overuse, poor footwear, and muscle imbalances.
Fortunately, there are several exercises that can help alleviate the pain and prevent further injury. Here are the three of the best exercises for shin splints:
1. Toe Raises
Toe raises are a simple yet effective exercise for strengthening the muscles in the front of the lower leg, which can help reduce the strain on the shinbone. To perform toe raises, stand with your feet hip-width apart and slowly raise up onto the balls of your feet, then lower back down. Aim for three sets of 15 repetitions, gradually increasing the number of sets as your strength improves.
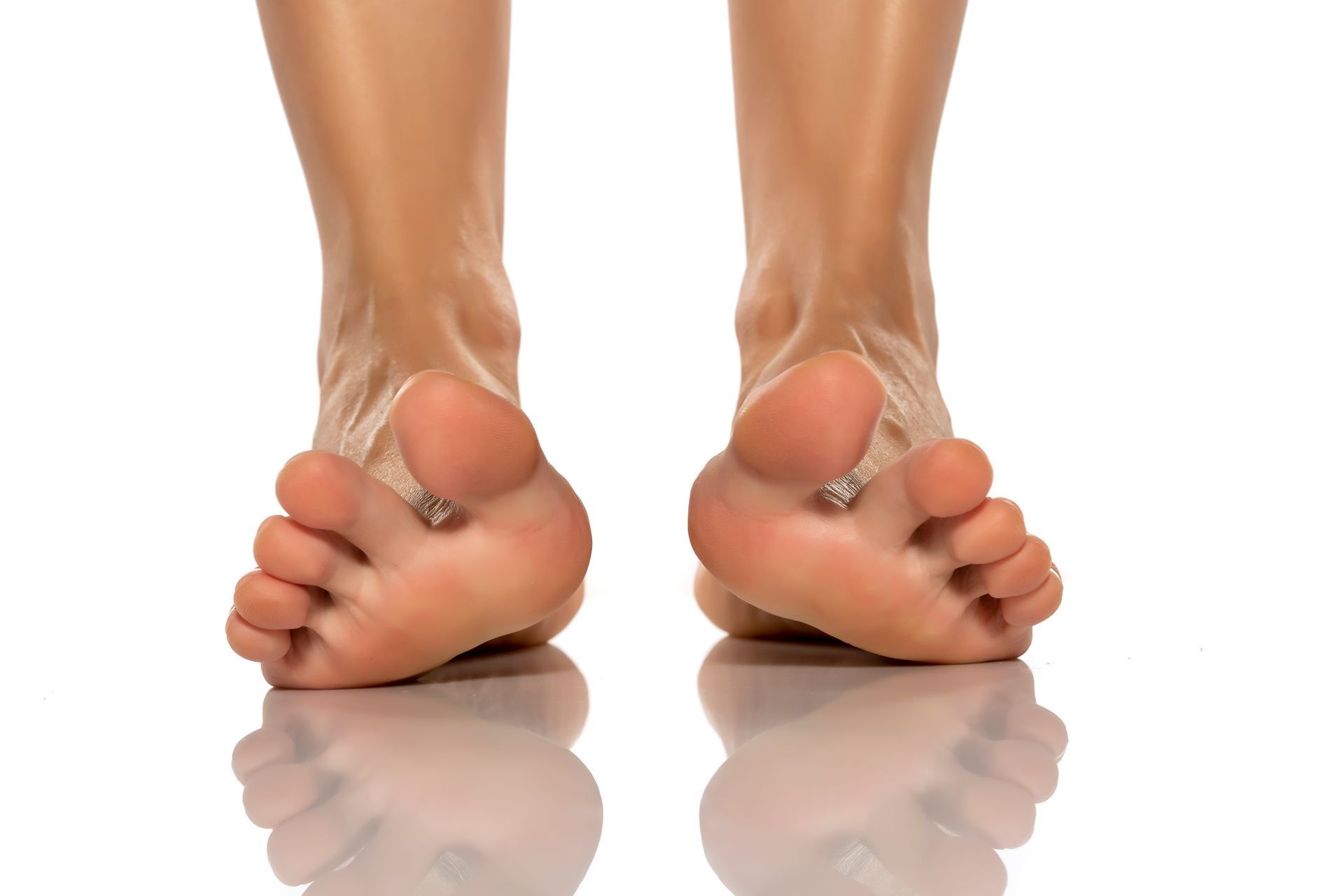

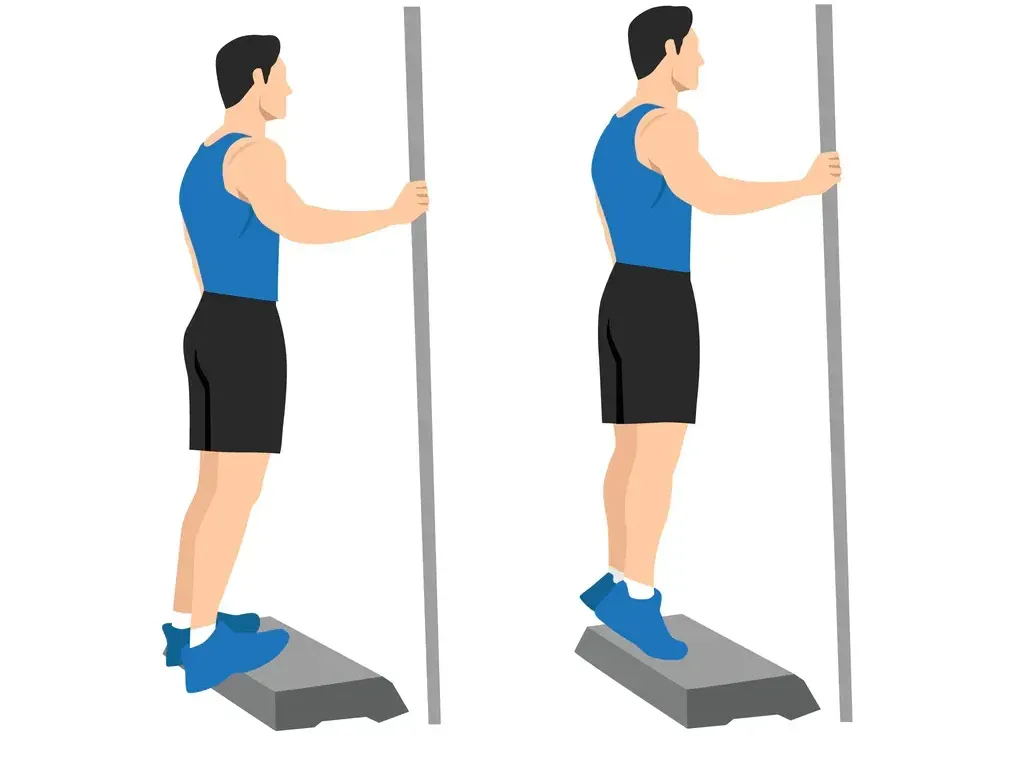
2. Heel Drops
Heel drops can help strengthen the muscles in the back of the lower leg, which can also help reduce the strain on the shinbone. To perform heel drops, stand on a step or other elevated surface with your heels hanging off the edge, then slowly lower your heels down as far as you can, then raise back up onto your toes. Aim for three sets of 15 repetitions, gradually increasing the number of sets as your strength improves.
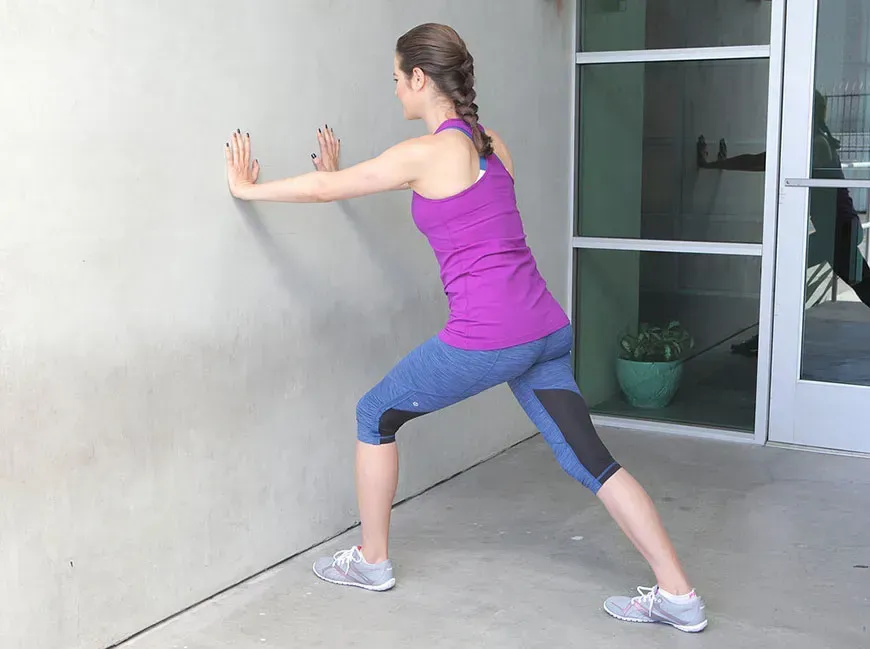
3. Wall Stretch
The wall stretch is a simple stretch that can help improve flexibility in the calf muscles, which can also help reduce strain on the shinbone. To perform the wall stretch, stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at shoulder height. Step one foot back and press your heel into the ground, keeping your knee straight. Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat.

Incorporating these exercises into your routine can help you manage and prevent shin splints. However, it's important to consult with a Physiotherapist or other healthcare professional if you experience persistent or severe pain, as there may be underlying issues that require further attention.
Chelmsford Physio
Riverside Leisure Centre, Victoria Rd, Chelmsford CM1 1FG